which example is a biomass energy source
Types of Biomass
Biomass refers to organic matter from plants and animals that can be converted into various forms of energy. In this article, we will explore different types of biomass and their significance in the field of renewable energy.
What is biomass?
Biomass is any organic matter derived from living or recently living organisms, including plants, animals, and their by-products. It is a renewable energy source that can be harnessed to produce electricity, heat, and biofuels.
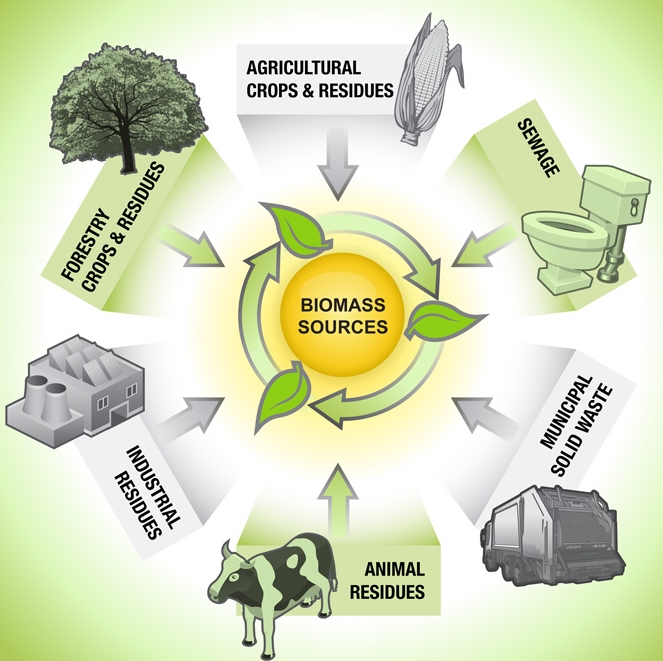
What are the sources of biomass?
Biomass can be derived from various sources. Some common sources include:
- Forestry residues like branches, bark, and wood chips.
- Agricultural residues such as corn stover, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse.
- Energy crops like switchgrass and miscanthus.
- Animal manure and organic waste from industries.

How is biomass used for energy production?
Biomass can be utilized for energy production through various processes such as:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned directly to produce heat and generate steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a gas mixture containing carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane, which can be used for electricity production or as a precursor for biofuels.
- Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used as a renewable fuel.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of bio-oil, biochar, and combustible gases.
What are the benefits of using biomass as an energy source?
The use of biomass as an energy source offers several advantages:
- Renewable: Biomass is derived from organic matter, making it a sustainable and replenishable energy source.
- Carbon neutral: When biomass is burned or converted, it releases carbon dioxide, but this is offset by the carbon absorbed by plants during their growth, making it carbon neutral.
- Diverse sources: Biomass can be derived from various sources, providing flexibility and abundant availability.
- Waste management: Utilizing biomass as an energy source helps in reducing waste and diverting organic matter from landfills.
- Local economy: Biomass energy production can create jobs and contribute to the development of local economies in rural areas.
What are the challenges associated with biomass utilization?
While biomass has several benefits, its utilization also comes with challenges:
- Supply and logistics: Biomass availability and transportation can pose challenges due to its bulkiness and seasonal variations.
- Efficiency: The conversion processes for biomass may not be as efficient as traditional fossil fuel technologies.
- Emissions: Although biomass is carbon neutral in the long run, the combustion or conversion of biomass can release pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
- Competition for land: Energy crops require agricultural land, which may lead to competition with food crops or natural habitats.
What are the future prospects of biomass energy?
Biomass energy holds promising potential for the future:
- Advanced technologies: Ongoing research focuses on improving biomass conversion technologies and increasing efficiency.
- Integration with other renewables: Biomass can be used in combination with solar and wind energy to provide a stable and reliable power supply.
- Waste-to-energy initiatives: Converting organic waste into biomass energy can contribute to waste management and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Job creation: The growth of the biomass energy sector can stimulate job creation and economic development in rural areas.
By exploring different types of biomass, understanding their sources, and recognizing the potential benefits and challenges associated with biomass energy, we can pave the way towards a sustainable and renewable energy future.