Imagine harnessing the sun's energy to power your camping gadgets, keep your boat battery topped off, or even run a small off-grid project. Small solar panels are making this dream a reality for more and more people, but knowing where to start can feel overwhelming.
It's easy to get lost in the technical jargon and myriad options when exploring small solar panels. Figuring out which type suits your specific needs, understanding their limitations, and avoiding common pitfalls can be a real challenge. Many find themselves unsure about power output, efficiency, and the best ways to integrate these panels into their chosen applications.
This guide aims to demystify the world of small solar panels, providing a comprehensive overview of the different types available, their ideal applications, and essential considerations for making informed purchasing decisions. We'll explore everything from portable chargers to DIY solar projects, equipping you with the knowledge to harness the sun's power in a small but significant way.
From crystalline silicon to thin-film technologies, we'll delve into the characteristics and uses of various small solar panels. We'll discuss the critical factors for choosing the right panel for your application, whether it's charging your phone on a hiking trip, powering a garden fountain, or supplementing the energy needs of a tiny home. Get ready to unlock the potential of small solar panels and discover how they can empower your life with clean, renewable energy. We will be covering topics like, portable solar panels, off-grid solar solutions, solar panel efficiency, small solar panel applications, renewable energy, DIY solar projects.
The Allure of Portable Solar Chargers
The goal of understanding the allure of portable solar chargers is to explore why these devices have become increasingly popular and essential for outdoor enthusiasts, travelers, and anyone seeking a reliable backup power source. We'll delve into the convenience, environmental benefits, and practical applications of portable solar chargers, showcasing their role in enhancing our on-the-go lifestyles.
I remember my first backpacking trip vividly. I was so excited to disconnect from the digital world, but soon realized my phone, my camera, and even my GPS relied on batteries. The thought of running out of power miles from civilization was daunting. That's when I started researching portable solar chargers. I opted for a foldable panel that could clip onto my backpack, and it was a game-changer. I could charge my devices while hiking, ensuring I always had a way to communicate and navigate. The peace of mind it offered was invaluable.
Portable solar chargers have revolutionized the way we interact with technology in outdoor settings. They come in various shapes and sizes, from compact panels that fit in your pocket to larger foldable models that can power multiple devices simultaneously. The key advantage is their ability to convert sunlight into electricity, allowing you to charge smartphones, tablets, cameras, and other USB-powered gadgets without needing a wall outlet. This is particularly useful for camping, hiking, and long-distance travel, where access to traditional power sources is limited.
Beyond their convenience, portable solar chargers contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle. By relying on solar energy, you reduce your dependence on fossil fuels and minimize your carbon footprint. This aligns with the growing global awareness of environmental issues and the desire to adopt eco-friendly practices. Many portable solar chargers are also designed with durability in mind, using rugged materials that can withstand the rigors of outdoor use. This ensures they can be reliable companions on all your adventures.
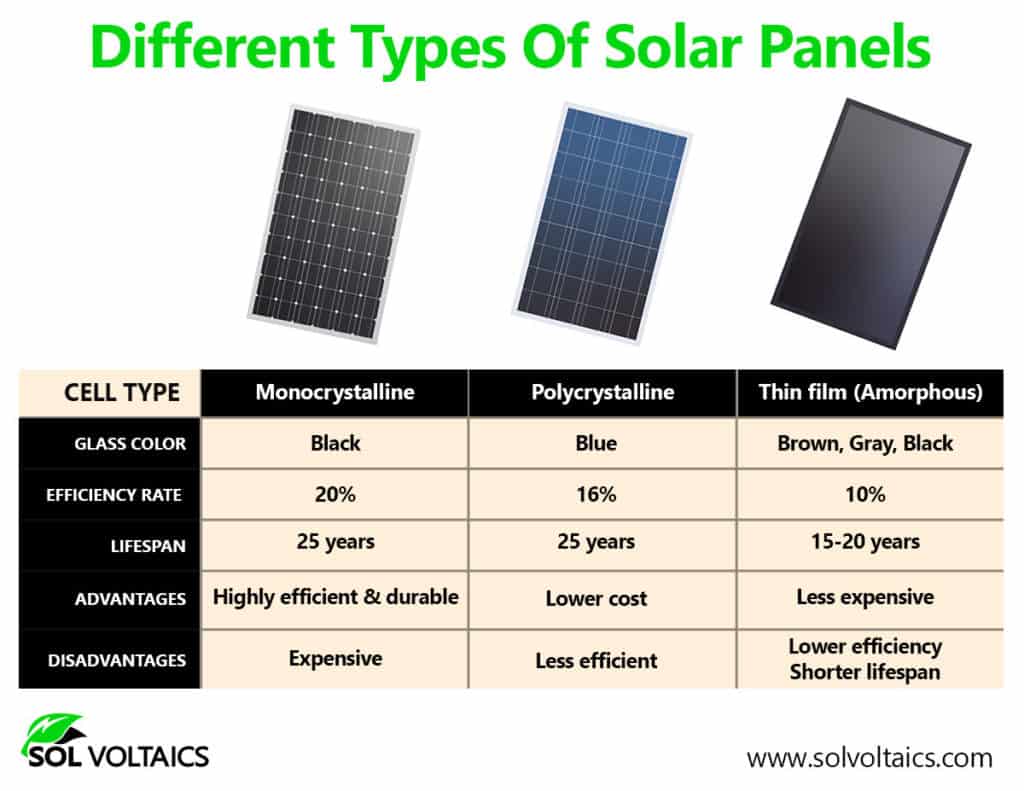
Demystifying Solar Panel Types: Crystalline vs. Thin-Film
The goal of demystifying solar panel types is to provide a clear and concise comparison between crystalline and thin-film solar panels. By highlighting their unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, we aim to help readers understand which type of panel is best suited for their specific needs and applications.
Small solar panels predominantly fall into two categories: crystalline silicon and thin-film. Crystalline silicon panels, including monocrystalline and polycrystalline variations, are known for their high efficiency and long lifespan. Monocrystalline panels, made from a single crystal of silicon, boast the highest efficiency rates, often exceeding 20%, but tend to be more expensive. Polycrystalline panels, made from multiple silicon crystals, offer a more cost-effective alternative with slightly lower efficiency.
Thin-film panels, on the other hand, are manufactured by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. They are typically more flexible and lightweight than crystalline silicon panels, making them suitable for unconventional applications like curved surfaces and portable devices. While their efficiency is generally lower, ranging from 10% to 15%, they can perform better in low-light conditions and are often more affordable.
Choosing between crystalline and thin-film panels depends on your specific requirements. If space is limited and high efficiency is crucial, crystalline silicon panels are the better choice. If flexibility, portability, and cost are primary concerns, thin-film panels may be more appropriate. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision and maximizing the benefits of your small solar panel setup.
A Brief History and the Myth of "Free Energy"
The goal of exploring the history and myth of "free energy" is to provide a historical context for solar energy development while debunking the misconception that it's a completely "free" resource. We'll discuss the evolution of solar technology, its associated costs, and the importance of responsible energy consumption.
The history of solar energy dates back to the 19th century, with early experiments demonstrating the photovoltaic effect – the conversion of sunlight into electricity. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that solar technology began to gain traction, driven by the space race and the need for reliable power sources in remote locations. The development of silicon solar cells revolutionized the industry, paving the way for more efficient and affordable solar panels.
While solar energy harnesses the sun's abundant power, it's a misconception to consider it entirely free.The production, installation, and maintenance of solar panels involve significant costs. These expenses include materials, manufacturing processes, labor, and ongoing monitoring. Additionally, solar panels have a limited lifespan, typically around 25-30 years, after which they need to be replaced or recycled.
Furthermore, the availability of solar energy is dependent on weather conditions and geographic location. Cloudy days and shaded areas can significantly reduce power output. To ensure a consistent energy supply, solar systems often require battery storage or grid connectivity, adding to the overall cost. While solar energy offers long-term savings and environmental benefits, it's important to understand the associated costs and limitations to make informed decisions about its implementation.
The Hidden Secret: Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency Ratings
The goal of uncovering the hidden secret of solar panel efficiency ratings is to explain what these ratings actually mean and how they influence the performance of small solar panels. We'll demystify the technical aspects, helping readers understand how to interpret efficiency ratings and make informed purchasing decisions based on their specific energy needs.
Solar panel efficiency ratings are a crucial but often misunderstood aspect of small solar panel technology. These ratings indicate the percentage of sunlight that a panel can convert into electricity. A higher efficiency rating means the panel can generate more power from the same amount of sunlight, making it more effective in limited space or low-light conditions.
However, it's important to note that efficiency ratings are measured under ideal laboratory conditions, which may not always reflect real-world performance. Factors such as temperature, shading, and panel angle can significantly impact the actual power output. Therefore, it's essential to consider these factors when evaluating solar panel efficiency ratings.
Another hidden secret is that the efficiency rating is just one piece of the puzzle. Other factors, such as the panel's power output, voltage, and current, also play a role in its overall performance. It's best to consider these factors together to determine the suitability of a solar panel for your specific application. By understanding the nuances of efficiency ratings, you can make more informed decisions and ensure that your small solar panel setup meets your energy needs effectively.
Recommendations for Choosing the Right Small Solar Panel
The goal of offering recommendations for choosing the right small solar panel is to provide practical guidance based on specific needs and applications. We'll cover key considerations such as power requirements, portability, durability, and budget, helping readers narrow down their options and select the most suitable panel for their intended use.
Choosing the right small solar panel involves several key considerations. First, assess your power requirements. Determine the wattage needed to power your devices or appliances, and choose a panel with sufficient output to meet those needs. Consider whether you'll be using the panel for occasional charging or continuous power supply.
Second, evaluate the importance of portability. If you plan to use the panel while hiking or camping, opt for a lightweight and foldable model that can easily fit in your backpack. For stationary applications, such as powering a garden fountain, a larger, more rigid panel may be more appropriate.
Third, consider the durability of the panel. Look for models made from rugged materials that can withstand the rigors of outdoor use. Water resistance and impact resistance are important features to consider, especially if you plan to use the panel in harsh environments. Finally, set a budget and compare prices from different manufacturers. While it's tempting to go for the cheapest option, investing in a higher-quality panel can save you money in the long run due to its increased efficiency and lifespan. By considering these recommendations, you can choose a small solar panel that meets your needs and provides reliable power for years to come.
Understanding Voltage, Amperage, and Wattage in Small Solar Panels
Understanding voltage, amperage, and wattage is essential for effectively using small solar panels. Voltage is the electrical potential difference, amperage is the current flow, and wattage is the power output (voltage x amperage). Matching the voltage requirements of your devices to the solar panel's output is crucial to prevent damage. For instance, charging a 12V battery requires a solar panel with a voltage slightly higher than 12V to compensate for losses. Amperage determines how quickly a device will charge; higher amperage means faster charging times. Wattage is the total power the solar panel can deliver. Selecting the right combination of these factors ensures efficient and safe use of small solar panels, whether for charging phones, powering lights, or running small appliances.
Tips for Maximizing the Efficiency of Your Small Solar Panel
The goal of providing tips for maximizing the efficiency of small solar panels is to offer practical advice on how to optimize their performance. We'll cover strategies for panel placement, maintenance, and storage, helping readers get the most out of their solar panels and ensure long-term reliability.
To maximize the efficiency of your small solar panel, start by positioning it optimally. Ensure that the panel receives direct sunlight throughout the day, avoiding any shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions. Adjust the angle of the panel to face the sun directly, especially as the sun's position changes throughout the year.
Regular maintenance is also crucial. Keep the panel clean by wiping it down with a soft cloth to remove dust, dirt, and debris that can reduce its efficiency. Check the wiring and connections regularly to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Store the panel in a dry, safe place when not in use to protect it from damage.
Consider using a solar charge controller to regulate the voltage and current flowing from the panel to your battery or device. This can prevent overcharging and extend the lifespan of your battery. By following these tips, you can maximize the efficiency of your small solar panel and enjoy reliable power for years to come.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Small Solar Panels
Troubleshooting common issues with small solar panels involves identifying and resolving problems that can hinder their performance. One frequent issue is reduced power output due to shading or dirt accumulation on the panel surface. Regularly cleaning the panel and ensuring it is placed in direct sunlight can solve this. Another common problem is faulty wiring or connections, which can be identified through visual inspection and testing with a multimeter. Damaged panels due to physical impacts or weather exposure can also lead to reduced efficiency or complete failure. Lastly, improper voltage matching between the solar panel and the device being charged can cause charging issues. Consulting the manufacturer's guidelines and using a compatible charge controller can help resolve these problems and ensure optimal solar panel performance.
Fun Facts About Small Solar Panels
The goal of sharing fun facts about small solar panels is to pique readers' interest and provide a lighthearted perspective on this technology. We'll uncover intriguing tidbits about solar energy, its applications, and its impact on the environment, making learning about solar panels an enjoyable experience.
Did you know that the first solar cell was invented in 1883 by Charles Fritts, who coated selenium with an extremely thin layer of gold? Or that solar panels were initially developed for use in space, powering satellites and spacecraft? These early applications paved the way for the widespread adoption of solar technology on Earth.
Here's another fun fact: solar panels can generate electricity even on cloudy days, although their output is reduced. This is because they can still capture diffuse sunlight. And while solar panels are often associated with rooftops, they can also be found on everything from watches and calculators to backpacks and tents.
Perhaps the most impressive fun fact is the potential of solar energy to meet the world's energy needs. The amount of solar energy that strikes the Earth in just one hour is more than the entire world consumes in a year. By harnessing this abundant resource, we can transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
How to Calculate Your Solar Panel Needs for a Specific Application
The goal of explaining how to calculate solar panel needs is to provide a step-by-step guide for determining the appropriate panel size and power output for a specific application. We'll cover essential calculations and considerations, empowering readers to accurately assess their energy requirements and select the right solar panel for their needs.
Calculating your solar panel needs involves several steps. First, determine the power consumption of the device or appliance you want to power. This is usually indicated in watts (W) on the device's label or manual. Next, estimate how many hours per day you plan to use the device. Multiply the power consumption by the usage hours to get the daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh).
For example, if you want to power a 10W LED light for 5 hours per day, the daily energy consumption is 10W x 5 hours = 50Wh. Now, consider the sunlight hours available in your location. This information can be found online or through local weather data. Divide the daily energy consumption by the sunlight hours to determine the required solar panel wattage.
In our example, if you have 4 sunlight hours per day, the required solar panel wattage is 50Wh / 4 hours = 12.5W. However, it's always a good idea to add a safety margin of 20-30% to account for losses and variations in sunlight. Therefore, you would need a solar panel with a wattage of around 15-16W. By following these steps, you can accurately calculate your solar panel needs and ensure that you have enough power to run your devices reliably.
What If Everyone Used Small Solar Panels?
The goal of exploring the hypothetical scenario of widespread small solar panel use is to examine the potential impacts on energy consumption, the environment, and society as a whole. We'll consider both the benefits and challenges of a world powered by small-scale solar energy.
Imagine a world where everyone utilized small solar panels to power their personal devices, small appliances, and even supplement their home energy needs. The impact on energy consumption would be significant. The demand for grid-supplied electricity would decrease, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. This would contribute to a cleaner environment and help mitigate climate change.
The widespread adoption of small solar panels could also empower individuals and communities. People would become more self-sufficient in terms of energy production, reducing their dependence on centralized power grids. This could lead to greater energy independence and resilience, especially in remote or underserved areas. Small solar panels could also create economic opportunities, such as manufacturing, installation, and maintenance jobs.
However, there would also be challenges to overcome. The production of solar panels requires resources and energy, and the disposal of old panels can create waste. It's important to ensure that the entire lifecycle of solar panels is sustainable. Additionally, widespread solar adoption would require changes to energy infrastructure and policies. But overall, the potential benefits of a world powered by small solar panels are substantial, making it a worthwhile goal to strive for.
Listicle: 5 Surprising Uses for Small Solar Panels
The goal of presenting a listicle of surprising uses for small solar panels is to showcase the versatility and innovation of this technology. We'll explore unconventional applications that demonstrate the potential of small solar panels to enhance various aspects of our lives.
Here are 5 surprising uses for small solar panels:
- Solar-powered backpacks: These backpacks feature integrated solar panels that can charge your phone or other devices while you're on the go.
- Solar garden fountains: Small solar panels can power water pumps in garden fountains, creating a relaxing and eco-friendly ambiance.
- Solar security cameras: These cameras use solar panels to recharge their batteries, allowing for wireless surveillance in remote locations.
- Solar e-bike chargers: Small solar panels can be attached to e-bikes to provide supplemental charging while riding, extending the range.
- Solar emergency kits: These kits include a small solar panel, a flashlight, and a USB charger, providing a reliable power source in case of emergencies.
These surprising uses demonstrate the versatility of small solar panels and their potential to enhance various aspects of our lives. From outdoor adventures to home security, small solar panels offer a sustainable and convenient power solution.
Question and Answer about Understanding the Different Types and Applications of Small Solar Panels
Q: What are the main differences between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels?
A: Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal of silicon, offering higher efficiency and a sleeker appearance, but they tend to be more expensive. Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon crystals, making them more cost-effective with slightly lower efficiency.
Q: How do I determine the wattage I need from a small solar panel?
A: Calculate the power consumption (in watts) of the device you want to power, then estimate the number of hours per day you'll use it. Multiply these two numbers to get the daily energy consumption in watt-hours. Divide this number by the average daily sunlight hours in your location to determine the required solar panel wattage. Remember to add a safety margin for inefficiencies.
Q: Can small solar panels work on cloudy days?
A: Yes, small solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, although their output will be significantly reduced compared to sunny conditions. They capture diffuse sunlight, but the power generated will be less efficient.
Q: Are small solar panels environmentally friendly?
A: Yes, small solar panels are generally considered environmentally friendly. They harness renewable energy from the sun, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. However, it's important to consider the environmental impact of the manufacturing process and the proper disposal of panels at the end of their lifespan.
Conclusion of Understanding the Different Types and Applications of Small Solar Panels
Exploring the world of small solar panels reveals a landscape of possibilities for sustainable energy solutions. We've journeyed through various panel types, from efficient crystalline to versatile thin-film, and highlighted their ideal applications, ranging from portable chargers to powering garden features. Understanding efficiency ratings, calculating your energy needs, and implementing best practices for maximizing performance are key to unlocking the full potential of these compact powerhouses. Embracing small solar panels is a step towards energy independence and a greener future, empowering individuals and communities to harness the sun's abundant energy.